|
|
Avulsion of the Lesser Trochanter
General Considerations
- Avulsion fractures result when the fracture fragment is pulled from its parent bone by forceful contraction of a tendon or ligament
- Avulsion fractures are most common in younger individuals engaging in athletic endeavors
- In the pelvis, the newly formed secondary centers of ossification, the apophyses, are the most likely portions of the bone to avulse
- Since the apophyses tend to form at the time of puberty, most of these pelvic avulsions occur at the time of puberty
- In general, they are uncommon injuries, seen almost exclusively in adolescent athletes with a 2:1 male to female preponderance
- They occur most often in track events like hurdling and sprinting, or games like soccer or tennis
- Most common to avulse is the ischial tuberosity followed by anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS) and the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) about equally
- Prompt diagnosis will prevent development of chronic pain
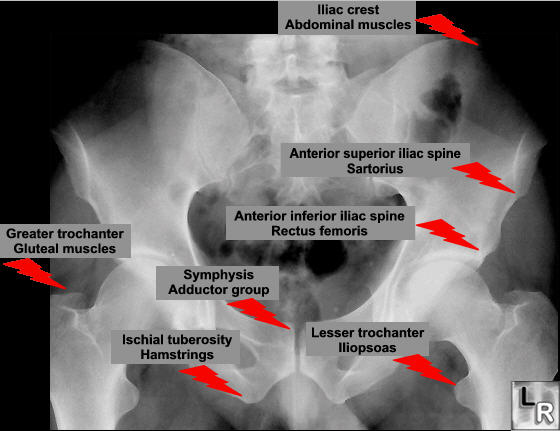
Pelvic Avulsion Fractures |
Avulsed Fragment |
Muscle that Inserts on that Fragment |
Anterior, superior iliac spine |
Sartorius muscle |
Anterior, inferior iliac spine |
Rectus femoris muscle |
Ischial tuberosity |
Hamstring muscles |
Lesser trochanter of femur |
Iliopsoas muscle |
Clinical findings
- Acutely, the athlete experiences sudden, shooting pain referred to the involved tuberosity
- They may lose muscular function
- Swelling and local tenderness may occur
- The clinical findings of the fracture are similar to those of soft tissue injuries to the muscles, tendons and ligaments and so may be initially missed
Imaging findings
- Since the apophyses occur in anatomically predictable locations, the findings are those of an avulsed bony fragment usually immediately adjacent to the parent bone
- Characteristic of these lesions is fracture healing with exuberant bony callus formation
- Can be confused with a bone tumor but must not be as an osteosarcoma and a healing fracture may appear similar pathologically
- Conventional radiography is the study of first choice
- If negative, magnetic resonance imaging may be helpful in demonstrating soft tissue injury, such as a tear of the tendon of the hamstring muscles
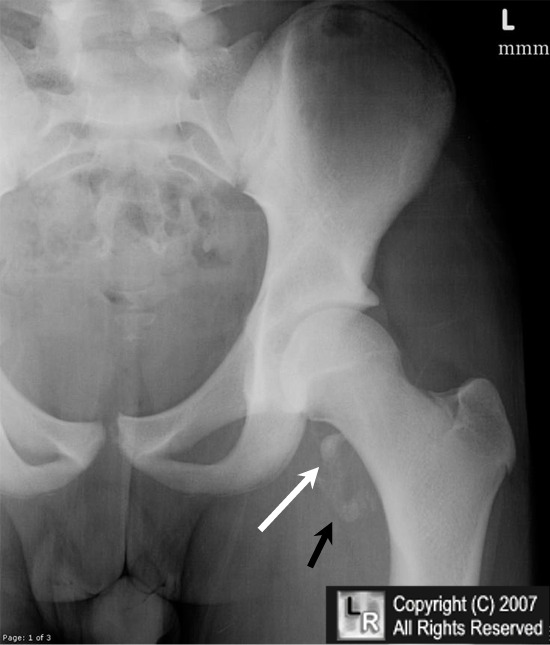
Avulsion Fracture of Lesser Trochanter of Femur. Frontal radiograph of the left hip demonstrates an avulsed
fragment of bone (white arrow) representing the lesser trochanter of the femur. The fracture is subacute
and heterotopic ossification (myositis ossificans) is forming in the soft tissues (black arrow)
.
For additional information about this disease, click on this icon if seen above.
For this same photo without arrows, click here
Avulsion fracture of the ischial tuberosity in adolescents—an easily missed diagnosis Gidwani, Jagiello, and Bircher BMJ 2004;329:99-100 (10 July), doi:10.1136/bmj.329.7457.99
|
|
|